RSI (Rapid Sequence Intubation) is a rare and highly critical procedure with the potential for serious complications. The main feature of any good program is the continuous assurance of quality. The purpose of a qualifier is to enable competent authorities to...
Rapid Sequence Intubation
Time course of procedures during rapid sequence intubation (RSI)
The procedure timeline for Rapid Sequence Intubation (RSI), which is used to safely place an endotracheal tube in patients, can be described as follows: Preparation and Inspection of Equipment: Inspection and preparation of all necessary medical devices and medicines....
Care after intubation (12.)
After securing the airway and stabilizing the endotracheal tube, post-intubation care for the patient begins. This care includes continuous monitoring of vital parameters, administration of drugs to maintain the patient's level of consciousness and neuromuscular...
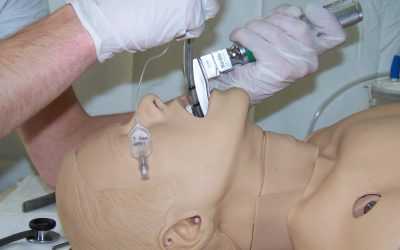
Intubation (11.)
Endotracheal intubation is a procedure to manage and secure the airway by placing an endotracheal tube directly into the trachea. It is also the most reliable airway securing technique that completely secures the airway and enables optimal ventilation and oxygenation...
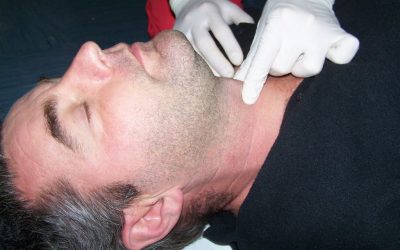
Protection and insurance of the respiratory tract (10.)
In the context of rapid sequence intubation (RSI) and airway management, protecting and securing the airway is a critical part of patient care. This involves various measures and techniques to ensure that the patient's airway remains open and that he receives adequate...
Sedation and paralysis (9.)
Sedatives used for sedation include barbiturates, opioids, benzodiazepines, nonsteroidal sedatives, and dissociative drugs. An ideal sedative should have a rapid onset of action, short-term loss of consciousness without cardiovascular effects. The sedative is applied...
Premedication (8.)
Medications initially administered to the patient are given to reduce physiological responses to subsequent intubation. These include bradycardia, tachycardia, increased intracranial and intraocular pressure, hypertension, hypoxia, and cough and gag reflexes....
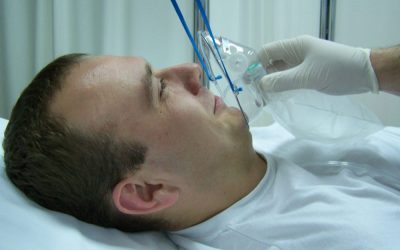
Preoxygenation (7.)
Even during the preparation of the patient, equipment, devices and supplies for the patient, we begin to perform pre-oxidation via a mask with an oxygen tank, providing 100% oxygen for three to five minutes before the intubation procedure. Proper preoxygenation will...
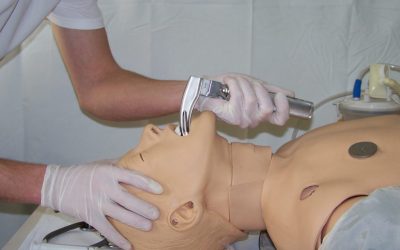
Procedure Intubation in rapid succession (6.)
Although the name of this technique, the "Rapid Sequence Intubation Procedure," suggests the rapid administration of drugs, the procedure itself is not rapid; it requires a certain amount of time. We've broken down this advanced airway management technique into seven...