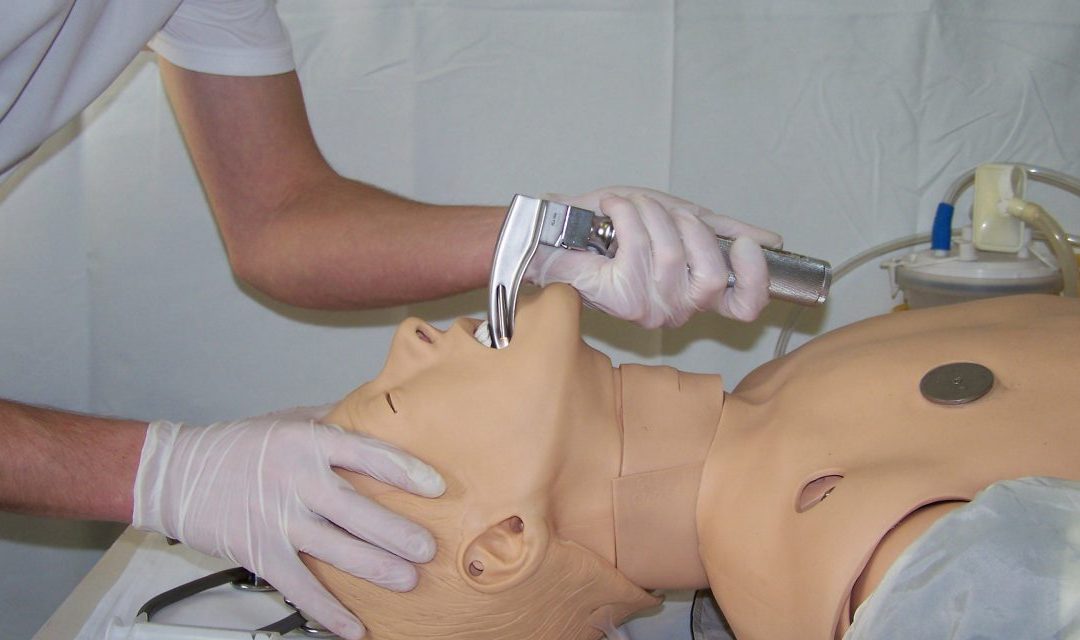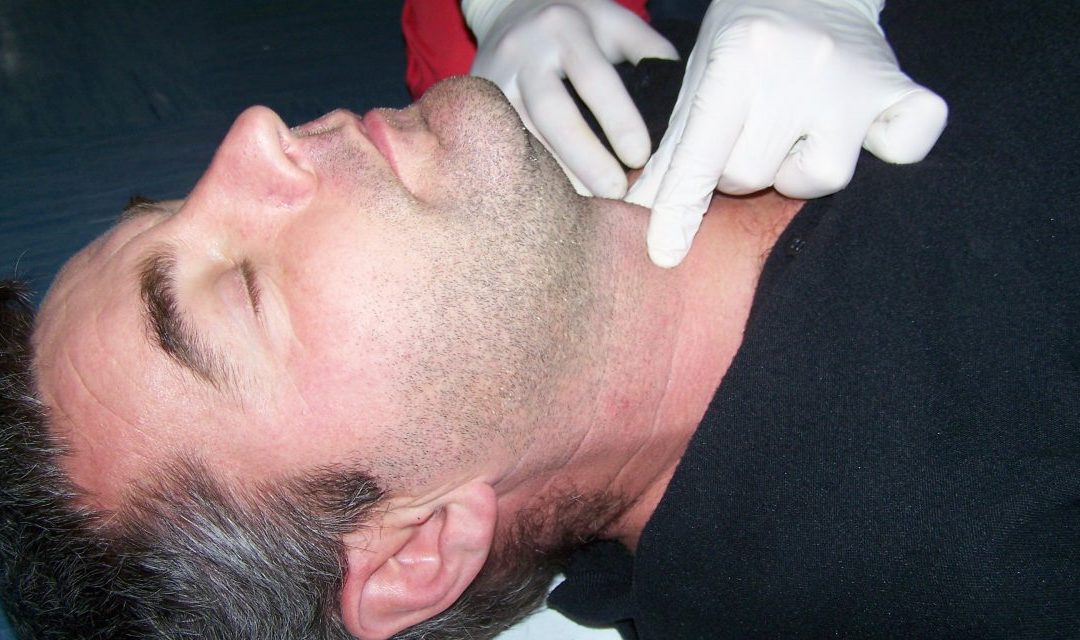

Sedation and paralysis (9.)
Sedatives used for sedation include barbiturates, opioids, benzodiazepines, nonsteroidal sedatives, and dissociative drugs. An ideal sedative should have a rapid onset of action, short-term loss of consciousness without cardiovascular effects. The sedative is applied...
Premedication (8.)
Medications initially administered to the patient are given to reduce physiological responses to subsequent intubation. These include bradycardia, tachycardia, increased intracranial and intraocular pressure, hypertension, hypoxia, and cough and gag reflexes....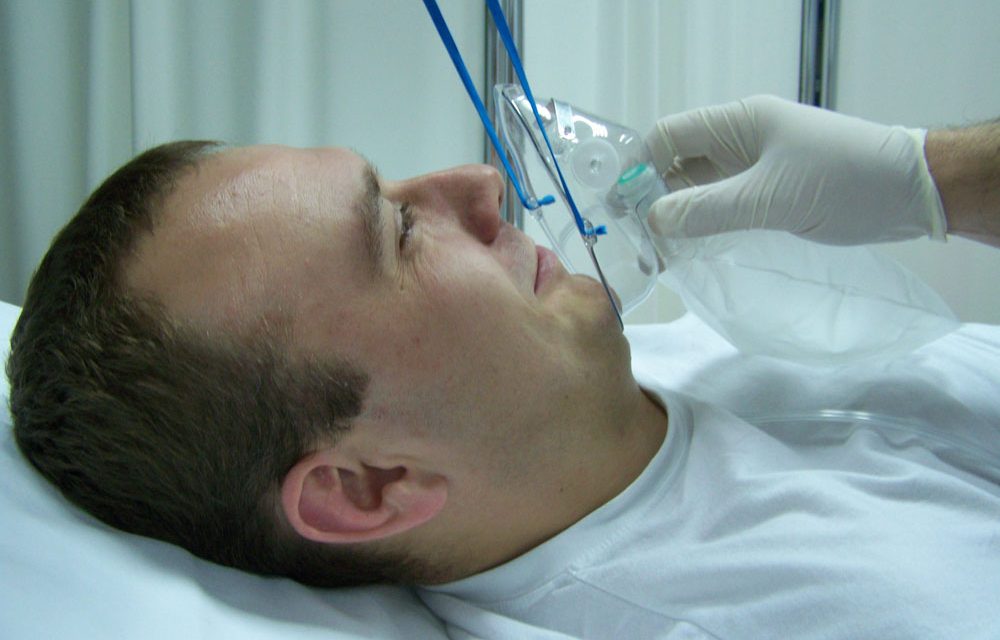
Preoxygenation (7.)
Even during the preparation of the patient, equipment, devices and supplies for the patient, we begin to perform pre-oxidation via a mask with an oxygen tank, providing 100% oxygen for three to five minutes before the intubation procedure. Proper preoxygenation will...