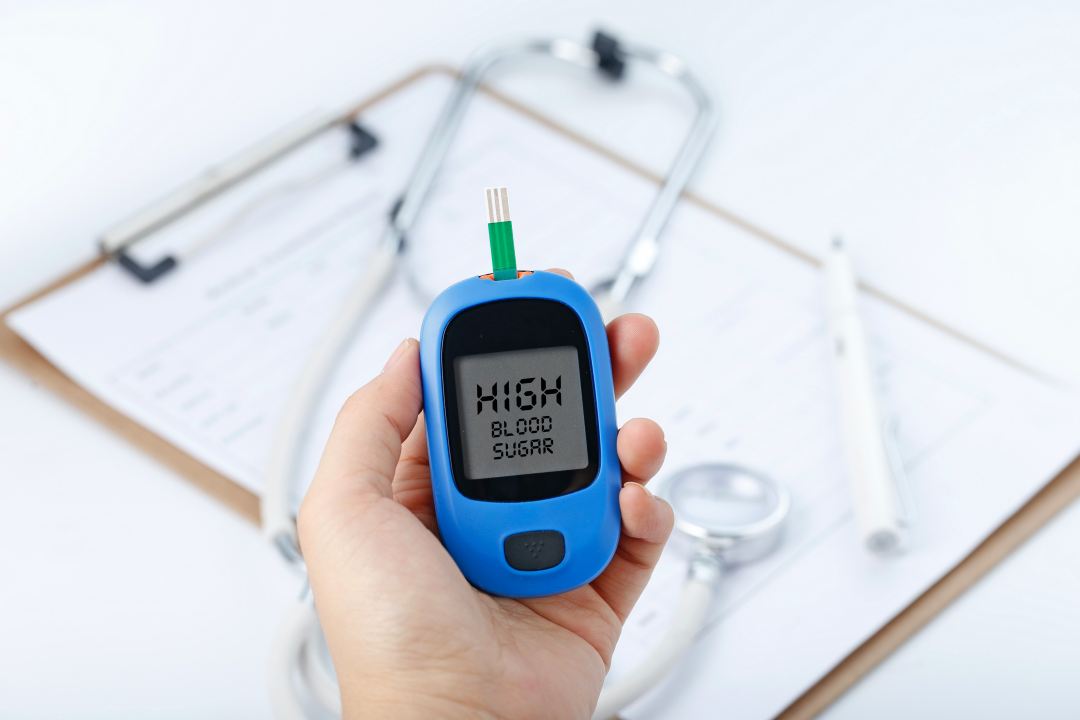
Hyperglycemia is a condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. Symptoms of hyperglycemia usually develop slowly and include thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening condition that belongs to the acute complications of diabetes. It occurs in patients with absolute or relative insulin deficiency, which leads to high hyperglycemia, accumulation of ketones, development of metabolic acidosis, copious urination, dehydration, and loss of sodium, potassium, and phosphate.
Common causes of diabetic ketoacidosis:
- Acute infections
- Urinary tract infections
- Accidental discontinuation of insulin treatment
- Undiagnosed disease onset
- Steroids can make the situation worse
Symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis:
- Increased urine output
- Increased thirst
- Increased appetite
Signs:
- Detection of the smell of acetone in exhaled breath
- Confusion, lethargy, loss of consciousness
- Dehydration, dry mouth, circulatory failure
- Hyperventilation Kussmaul breathing
- Weight loss
Management of hyperglycemia:
- Assess safety and eliminate risks for both yourself and the patient.
- Assess the patient using the ABCDE approach.
- Measure blood glucose level.
- Assess for dehydration.
- Give oxygen.
- Establish venous access.
- Monitor the patient (monitoring ECG, SaO2, blood pressure, vital signs).
- Give IV crystalloids (if significant dehydration is present, give 250 ml crystalloid boluses and reassess vital signs).
- Record all procedures performed.
- Transport patient to hospital for insulin therapy and fluid/electrolyte therapy.


0 Comments