On the nasal catheter, oxygen flows from 1 l/min to a maximum of 6 l/min, achieving oxygen concentrations in the range of 24-44%. It is usually not suitable for unstable patients in emergency situations because high oxygen concentrations cannot be achieved.
Equipment:
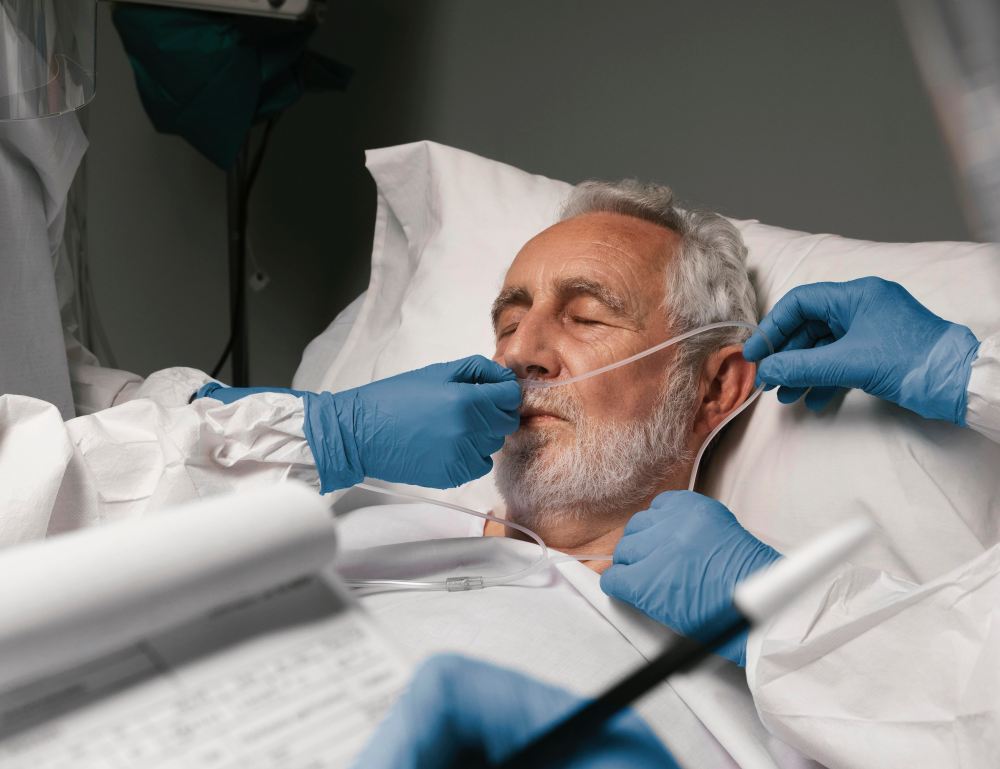
Personal protective equipment – mandatory protective gloves, and in the presence of coughing or other bodily fluids, a protective mask and glasses. Oxygen cylinder and flow meter. An appropriately sized nasal probe.
Procedure:
- Apply personal protective measures.
- Check the amount of oxygen in the cylinder and ensure that the pressure is within the allowable limits.
- Introduce yourself to the patient if you have not already done so, explain the reasons and procedure for placing the nasal probe.
- Connect the nasal catheter tubing to the flow meter extension and set the flow between 1 l/min and 6 l/min.
- Place both extensions into the patient’s nostrils, making sure they curve downward for comfort. Route the catheter tubing over the patient’s ears and secure it under the chin, not behind the head, to avoid pinching the tubing and reducing flow.
- Record all actions in the medical documentation (see Medical documentation).
Important: Do not apply an oxygen flow greater than 6 l/min. Although generally better tolerated than an oxygen mask, a nasal catheter can cause patient discomfort. It is important to explain the reason and expected benefits of its use.


0 Comments